1. Introduction
ENOS Firewall is a cyber security management system based on Linux iptables, providing comprehensive network access control and security protection for routers.
Network Zone Management
- LAN Zone: Free communication between intranet devices
- WAN Zone: Extranet access control, default to block active connections
- DMZ Zone: Isolated Server Zone
Port Control
- Port Open: Allow specific services to provide external access
- Port Forwarding: Forward extranet requests to intranet devices
- Port Blocking: Prevent Unnecessary Network Services
Traffic forwarding
- NAT Translation: Internal network devices share an extranet IP to access the Internet
- Traffic forwarding rules: Control data flow between different network zones
2. Configuration steps
Basic Area Configuration
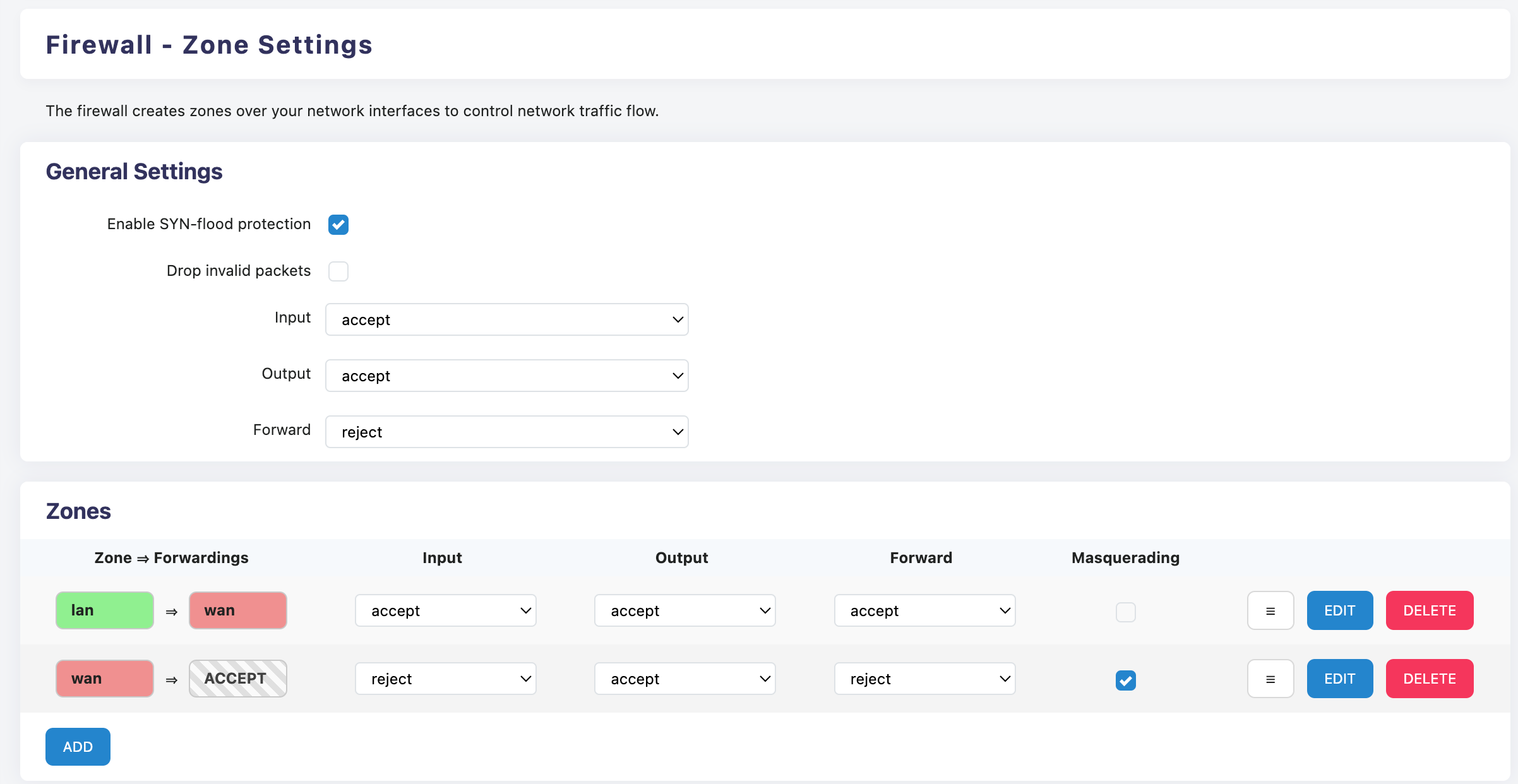
The regional configuration page is divided into global settings and zone settings.
Global settings are the fundamental behavior of the firewall system, equivalent to the 'fallback rules' of the firewall, and are used when there are no matching rules.
Zone settings are refined controls for specific network interfaces divided by zones. 'Masquerading' can be regarded as one-way NAT.
The gray zone ACCEPT in the regional settings refers to any region.
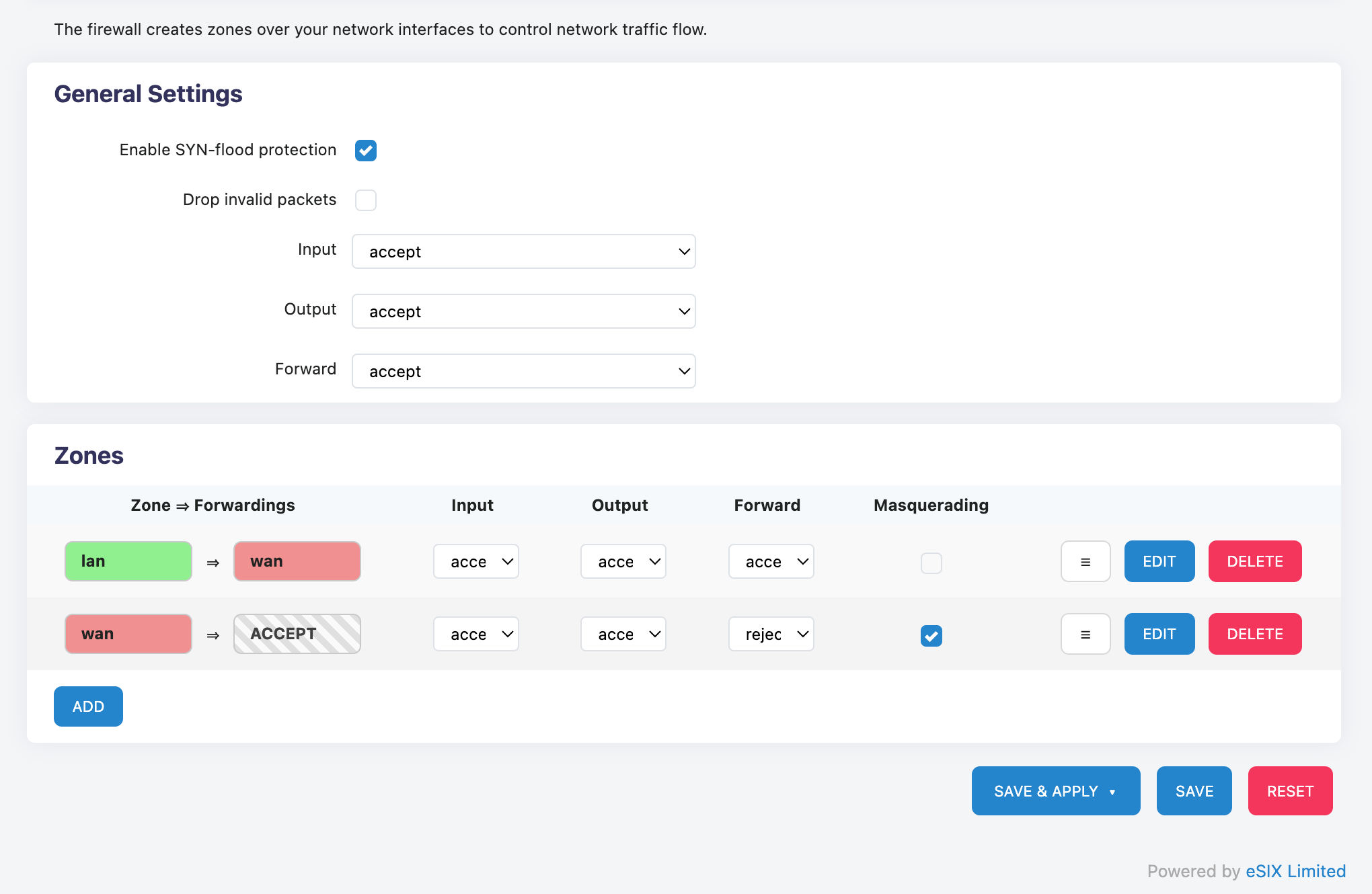
Click EDIT to perform detailed configuration on the zone, including interface zone settings, forwarding rule settings, etc.
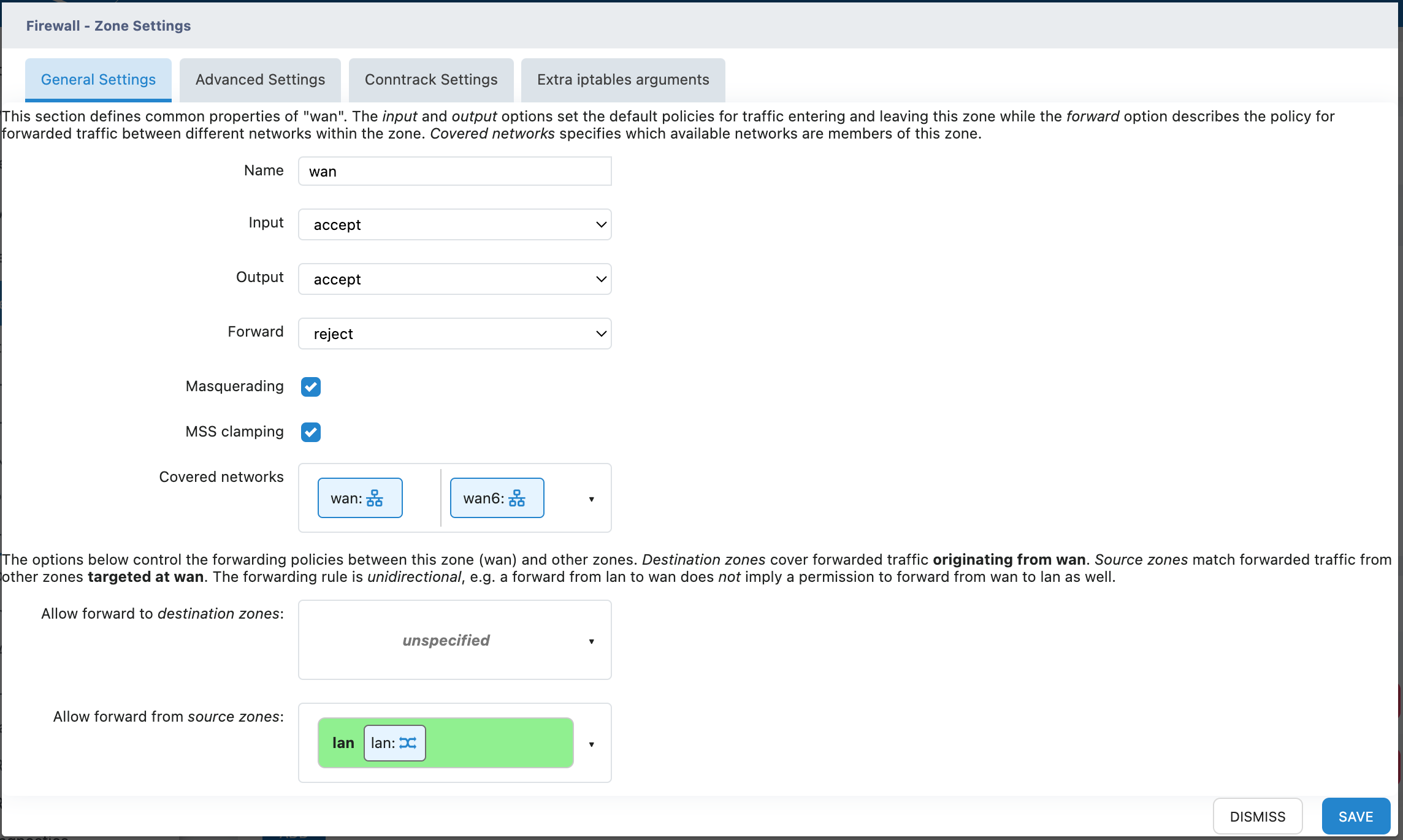
Recommended default settings
3. Port Forwarding
1. Name
- Recommended to fill in: Descriptive Name
Example:
- "NAS Access"
- "Camera Monitoring"
- "Game Server"
- "Remote Desktop"
2. Protocol
TCP: Web pages, file transfer, remote desktop, etc.
UDP: Games, video streaming, DNS, etc.
TCP + UDP: Services that require both protocols simultaneously.
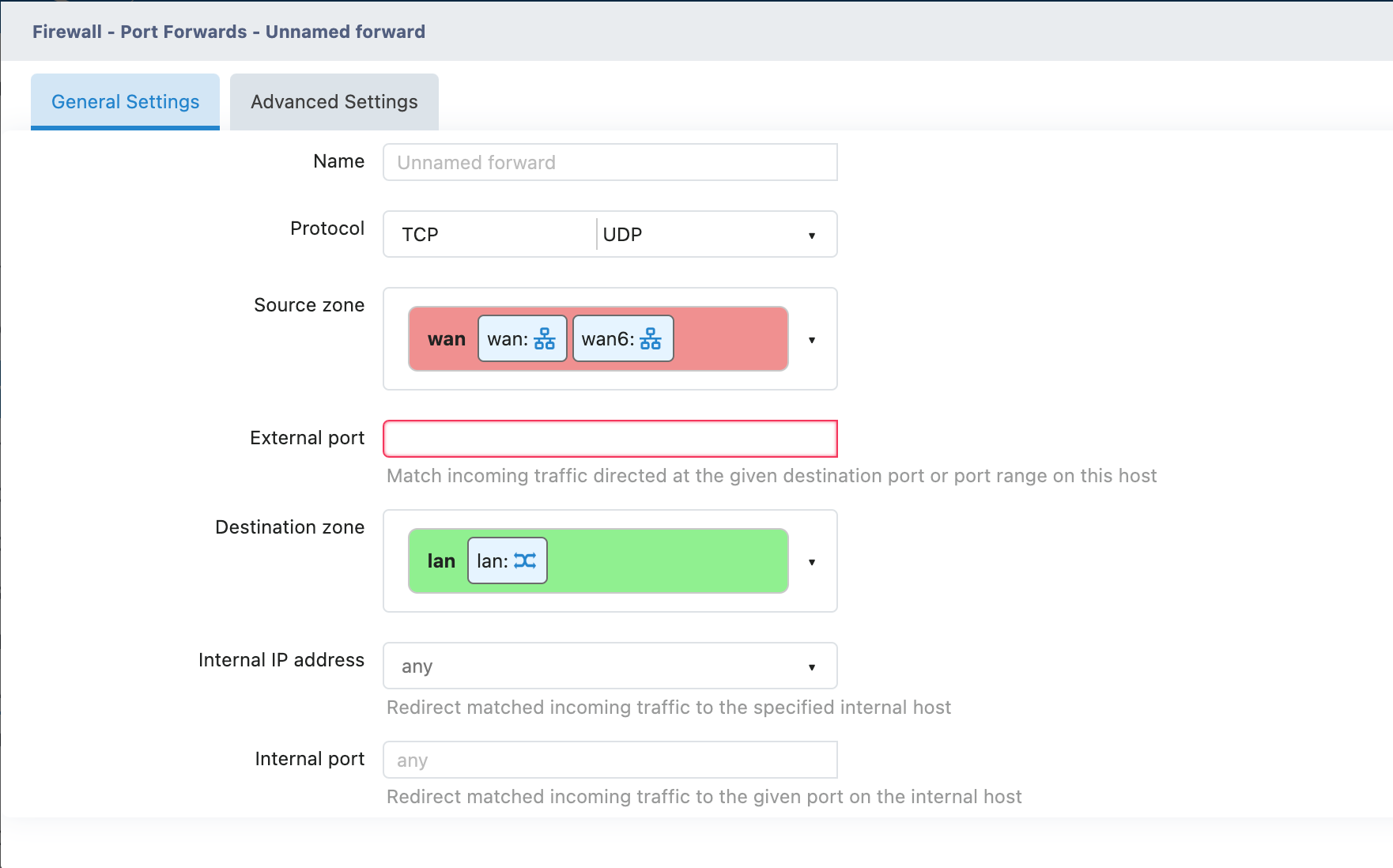
3. Source zone (Source Area)
Default Selection: wan (extranet)
Meaning: Allows access from which network area
4. External Port
Function: Port Number used for extranet access
Example:
8080 (Common Web Port) - 3389 (Windows Remote Desktop) - 22 (SSH) - 21 (FTP)
5. Destination zone (Target Area)
Default Selection: lan (intranet)
Meaning: Forward to which network area
6. Internal IP Address
Fill in: Internal IP of the target device
Example:
192.168.1.100 (NAS device) - 192.168.1.50 (surveillance camera) - 192.168.1.10 (game console)
7. Internal port
Fill in: The port actually used by the target device
can be the same as or different from the External port
4. Actual Configuration Example 1
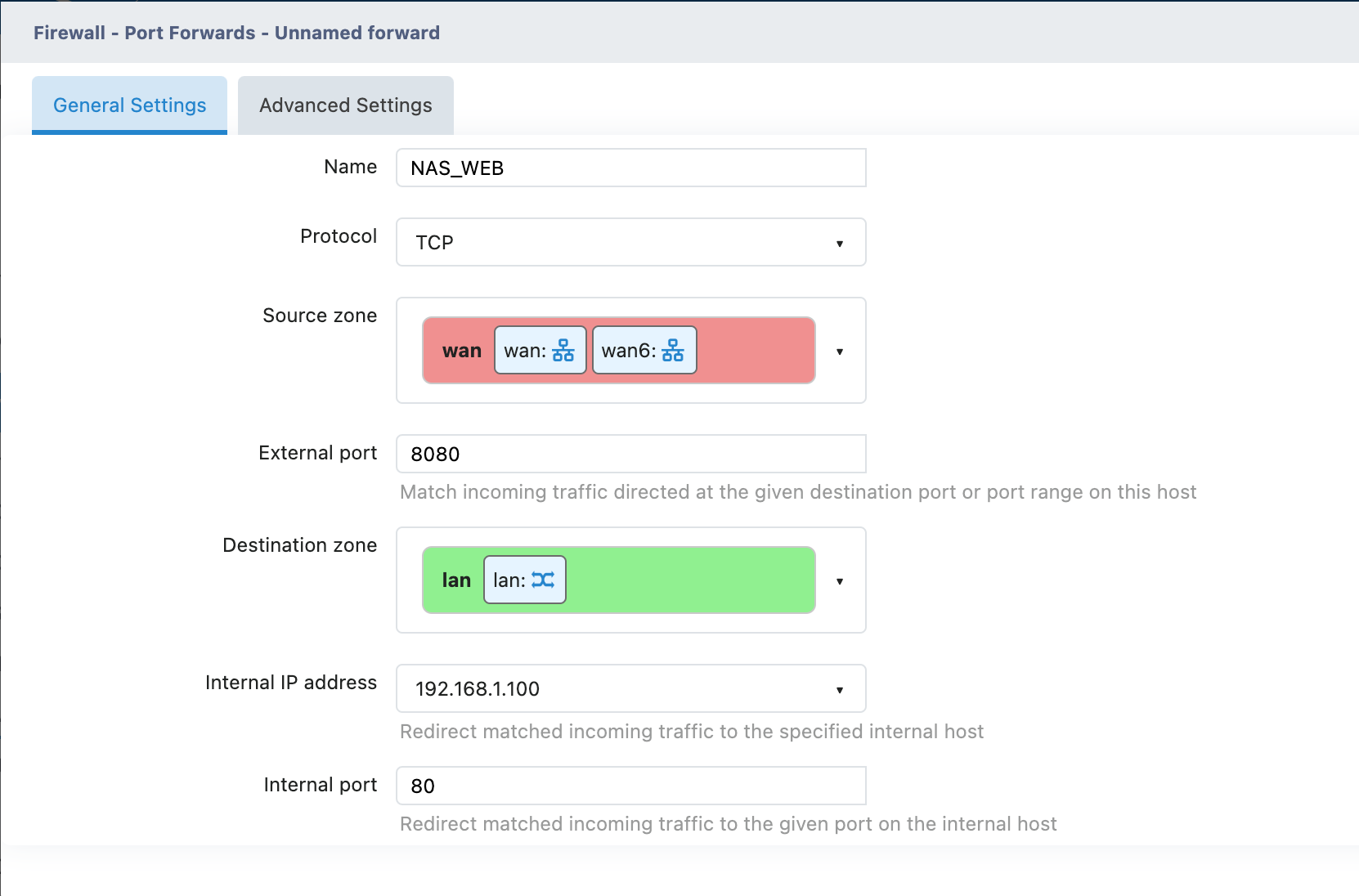
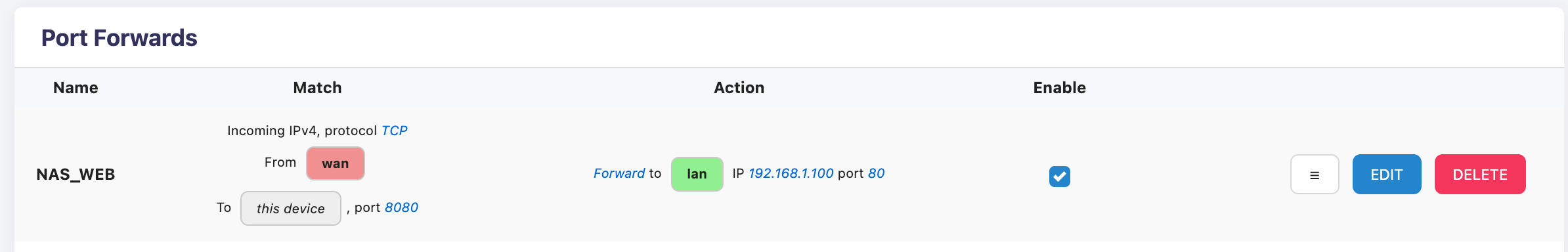
Example: Open NAS Access
Requirement: Allow the extranet to access the Web interface of the intranet NAS through port 8080
Access Method: http://WAN IP:8080
Traffic Rules
Traffic Rules is the most flexible feature in the ENOS system firewall, which can precisely control the flow of data packets between different network zones.
⚠️ Warning
It is not recommended to make any modifications to the rules set by the system default settings to avoid creating new issues.
Traffic rules are matched according to the priority from top to bottom, and the priority can be adjusted by dragging the button in the illustration.
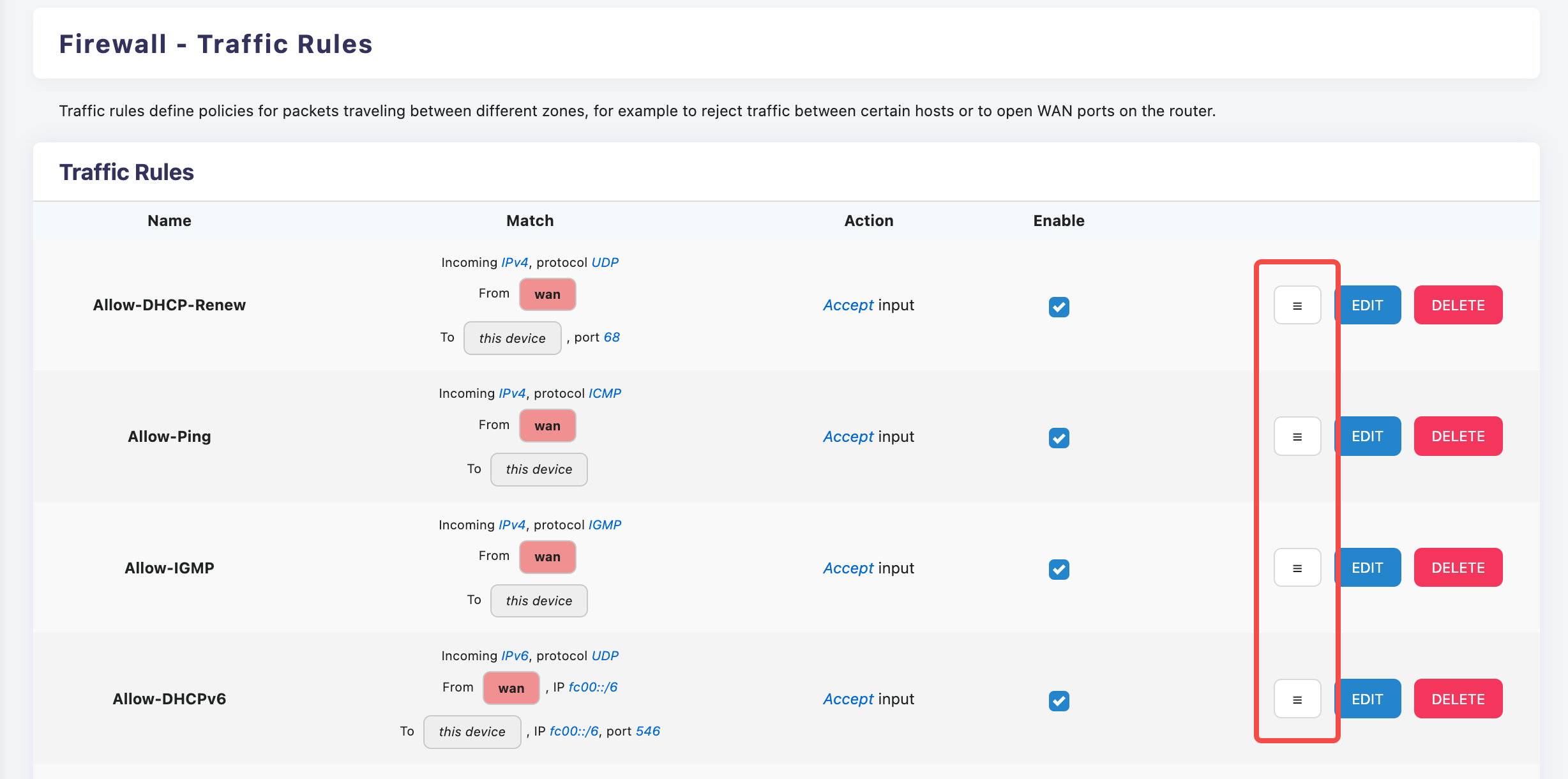
Add a new rule
Click the ADD button on the page to open the new rule page.
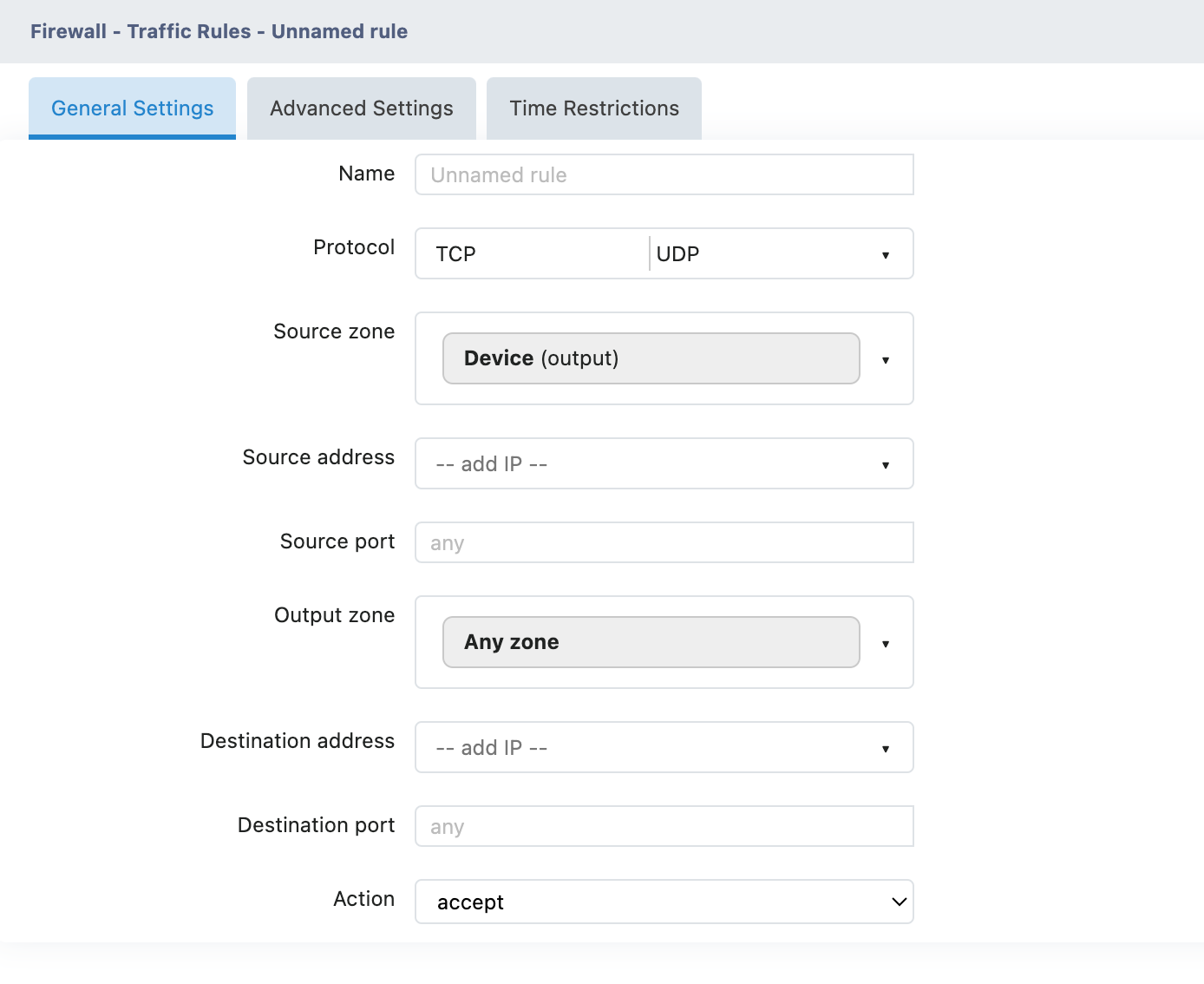
Basic Information
Name: Rule name (it is recommended to use a descriptive name)
Action: Data processing method (drop/accept/reject/don't track, etc.)
Match Condition
Protocol: Protocol type (TCP/UDP/ICMP/ ALL , etc.)
Source zone: Source network zone
Source address : source IP address or network segment
Source port: source port
Destination zone: target network area
Destination address : Destination IP Address or network segment
Destination port: destination port
5. Actual Configuration Example 2
Example 1: Prohibit specific devices from accessing the Internet
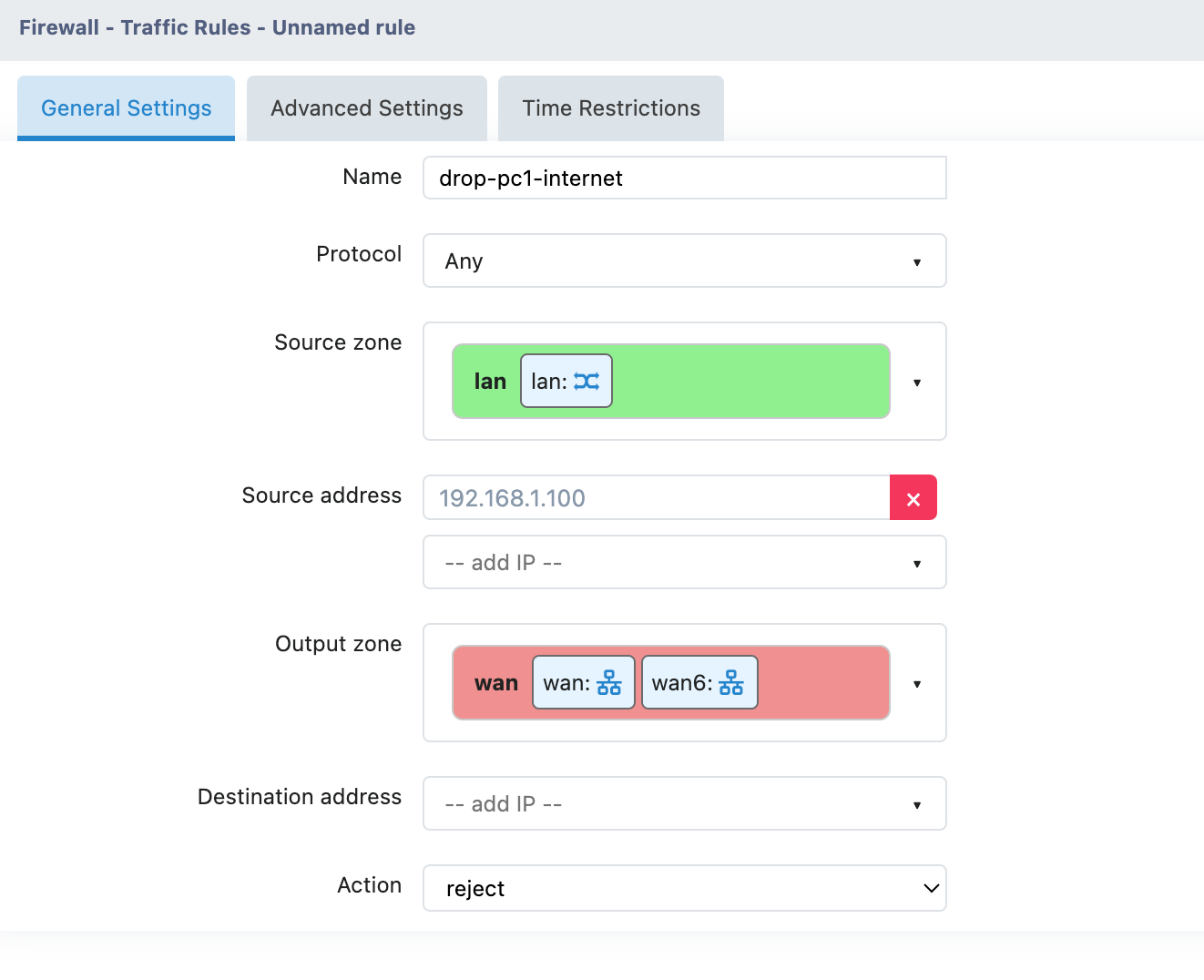

NAT Rules
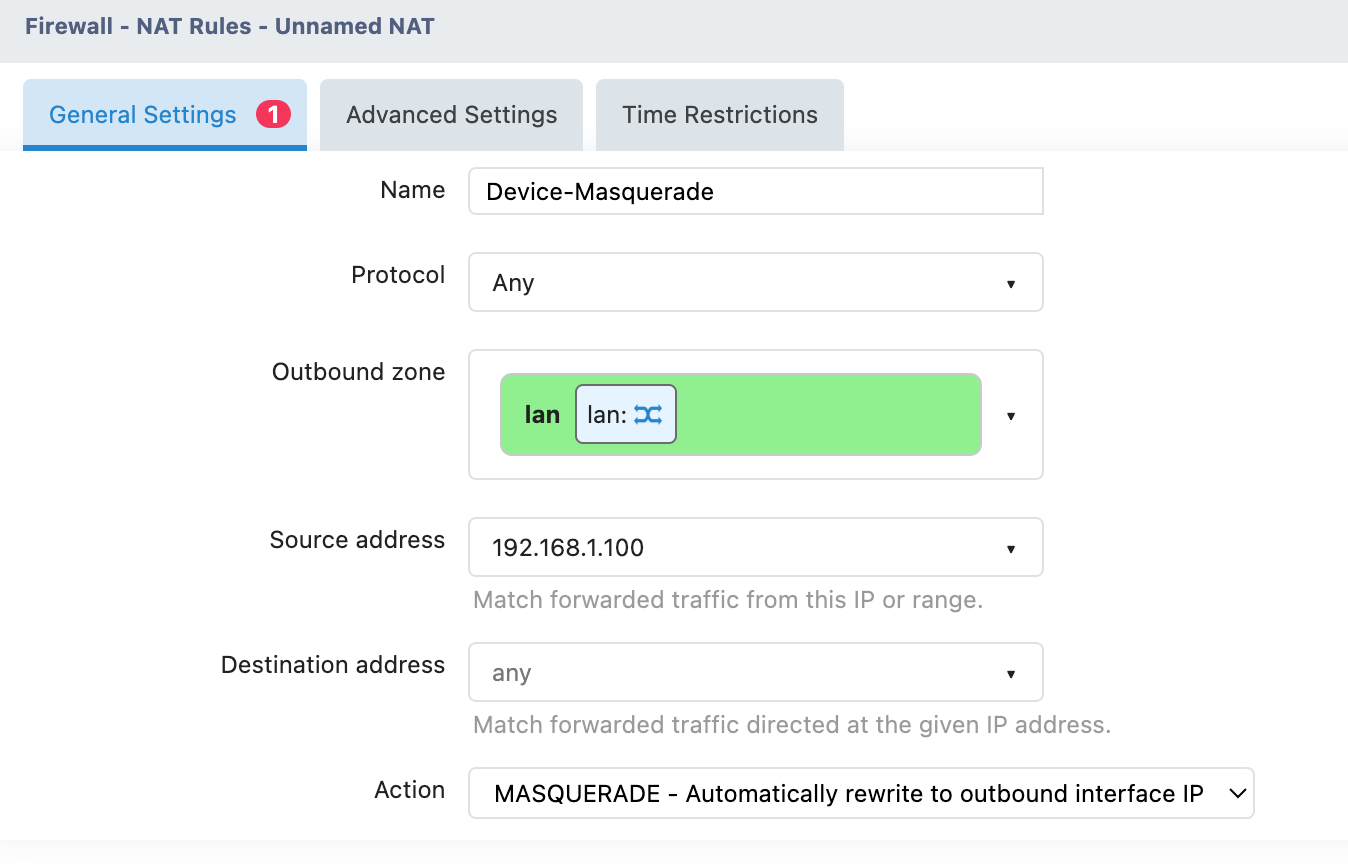
NAT Rules (Network Address Translation Rules) are one of the advanced features in a firewall, which allow you to precisely control the source IP Address used for outbound and forwarded traffic.
Functions of NAT
| Function | Explanation | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Address Conversion | Converting Internal IP to Public IP | Basic internet needs |
| Port Conversion | Modify the source port number | Avoid port conflicts |
| Load Balancing | Assign different outbound IPs | Multi-WAN Environment |
| Traffic Camouflage | Modify source address | Special Network Requirements |
Configuration Instructions
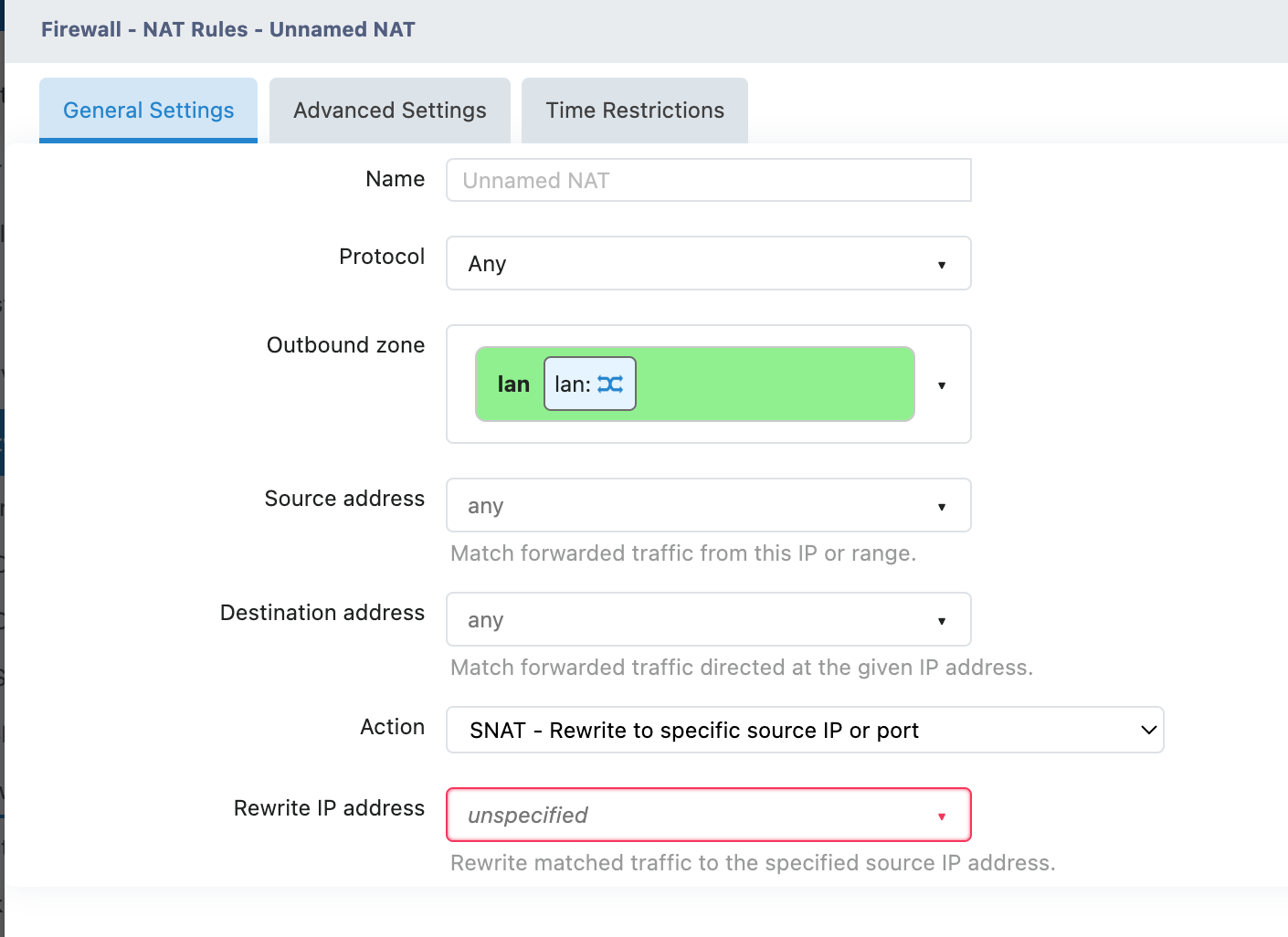
| Name | Specify a descriptive name for the rule | |
| Protocol | TCP/UDP/ICMP/Any (All Protocols) | |
| Outbound zone | From which network area does the traffic exit | |
| Source address | Match traffic from a specific source IP Address | |
| Destination address | Match traffic accessing a specific target | |
| Action | SNAT | Rewrite to the specified IP/Port |
| MASQUERADE | Automatically use the IP address of the export interface | |
| ACCEPT | Do not perform address translation | |
| Rewrite IP address | Specify a new source IP Address | |
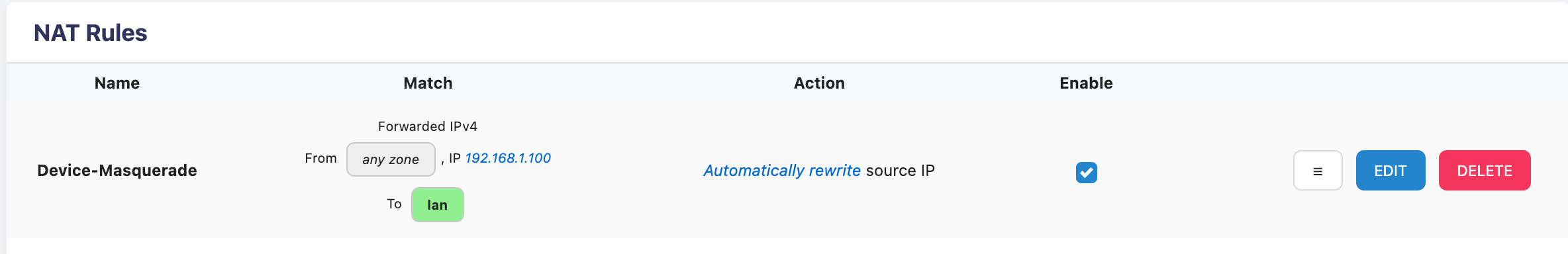
6. Actual Configuration Example 3
Example: Source Address Spoofing
Requirement: Make the device at 192.168.1.100 appear to be going out from the WAN port IP Address