Introduction
VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) is a network virtualization technology that allows multiple independent routing table instances to be created on a single physical router, enabling network isolation.
Usage Scenarios
Network Isolation
- Create independent network environments for different departments or clients
- Prevent routing information leakage between different VRFs
Service Separation
- Separate management traffic from business traffic
- Create a dedicated network channel for specific services
Configuration steps
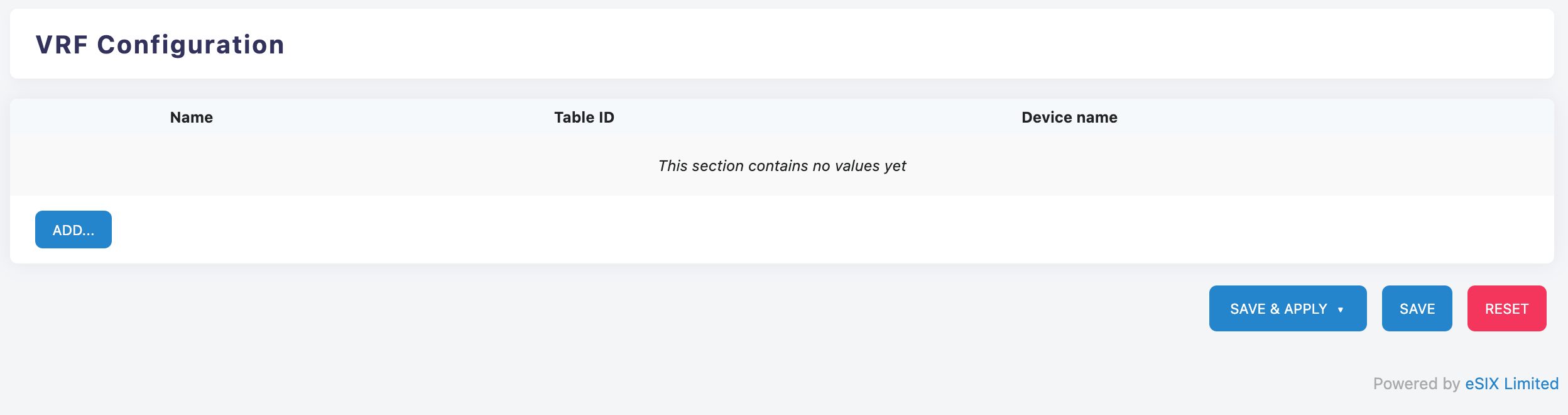
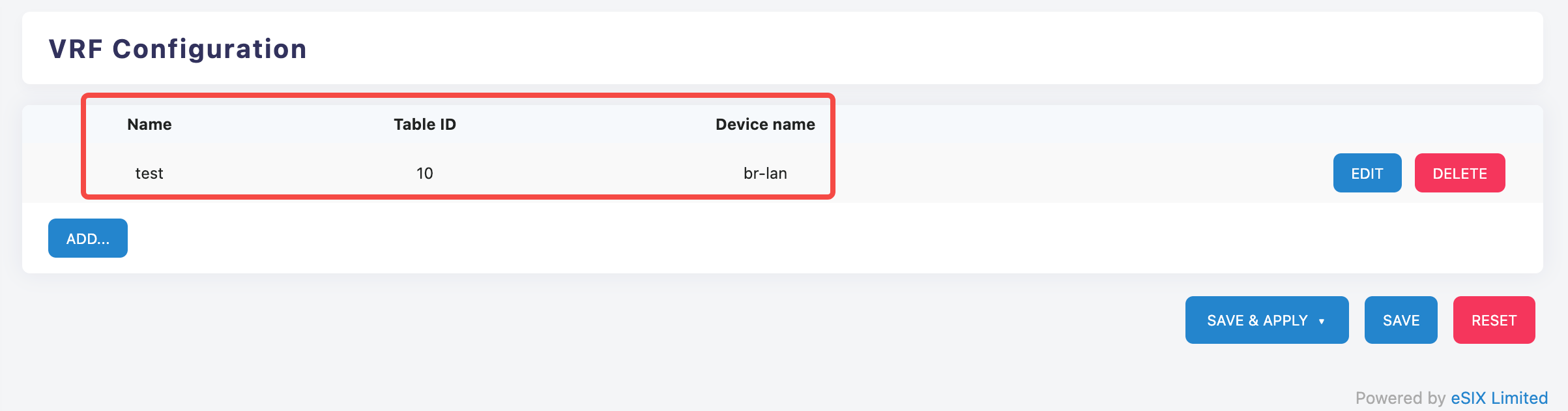
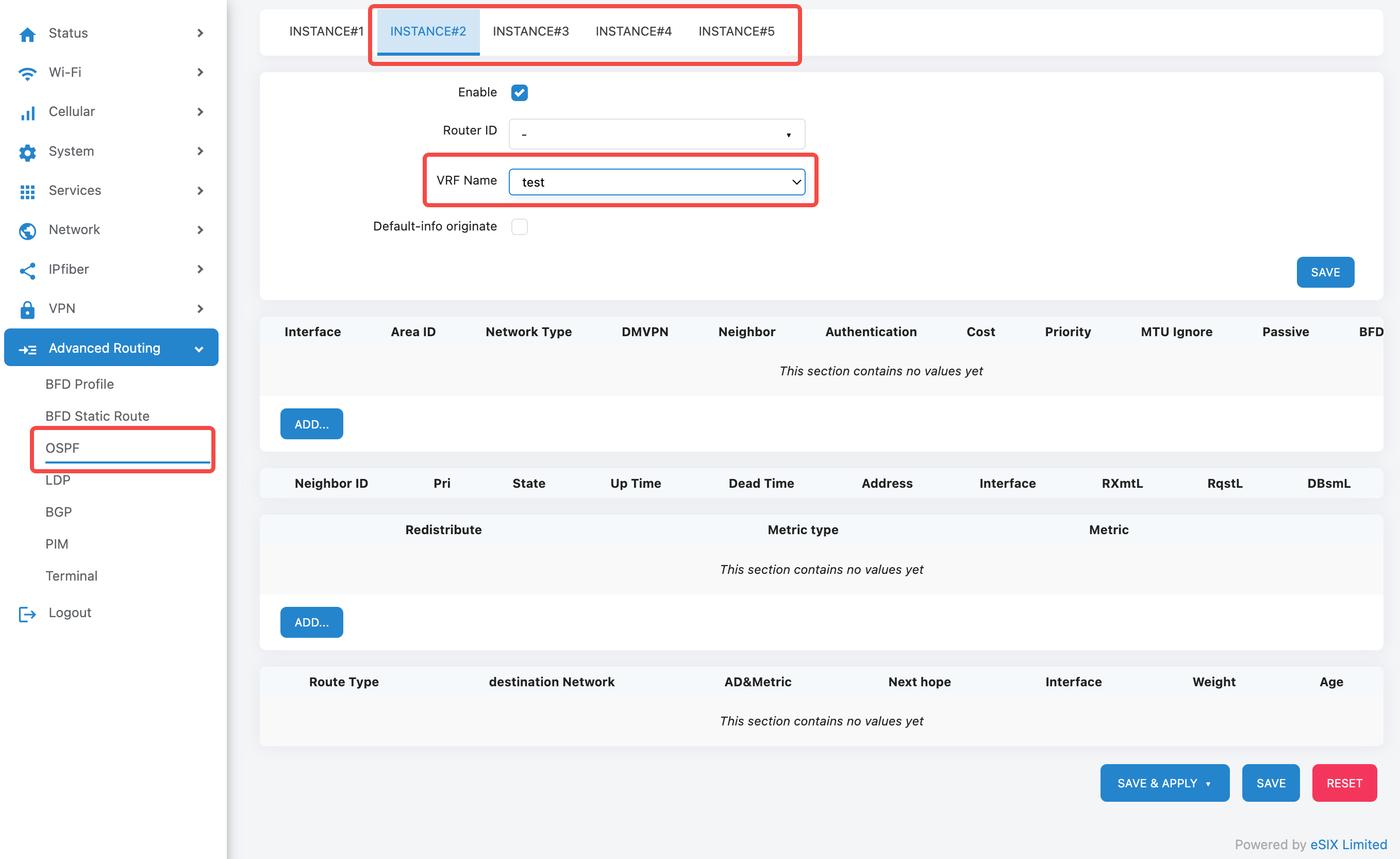
VRF Configuration Interface
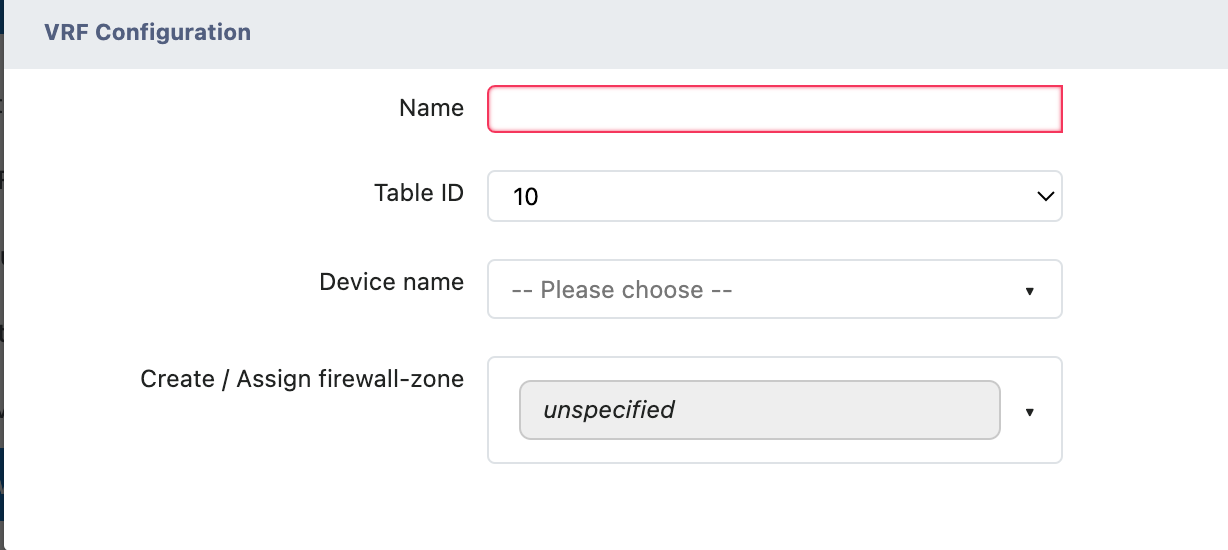
The VRF configuration interface includes the following main fields:
- Basic Configuration Fields
- Name: Unique identifier name of the VRF instance
- Table ID (Routing Table ID): Specifies the routing table number used by the VRF (e.g., "10" in the example)
- Device name: Select the associated network device
- Advanced Configuration Options
- Create / Assign firewall-zone (Create / Assign Firewall Zone):
- Default value: unspecified (not specified)
- can be used to associate a VRF with a specific firewall security zone
Operating Steps
Create a new VRF instance
Add VRF
- Click the "ADD..." button to start creating a new VRF configuration
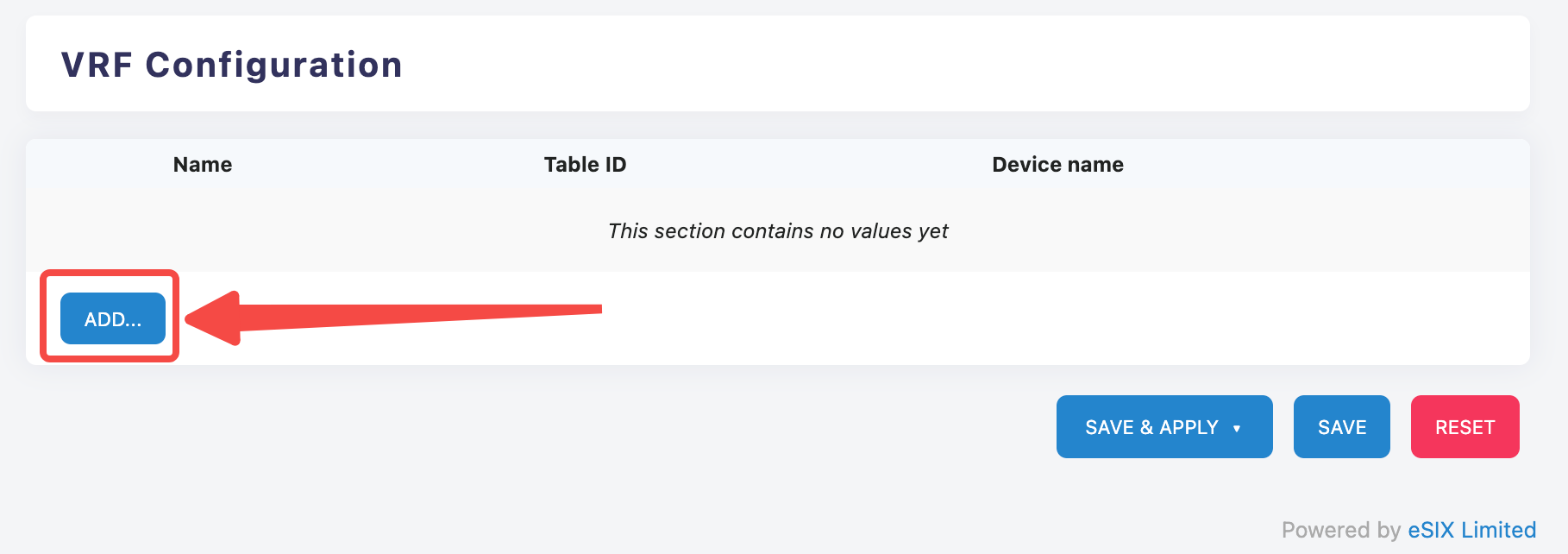
- Click the "ADD..." button to start creating a new VRF configuration
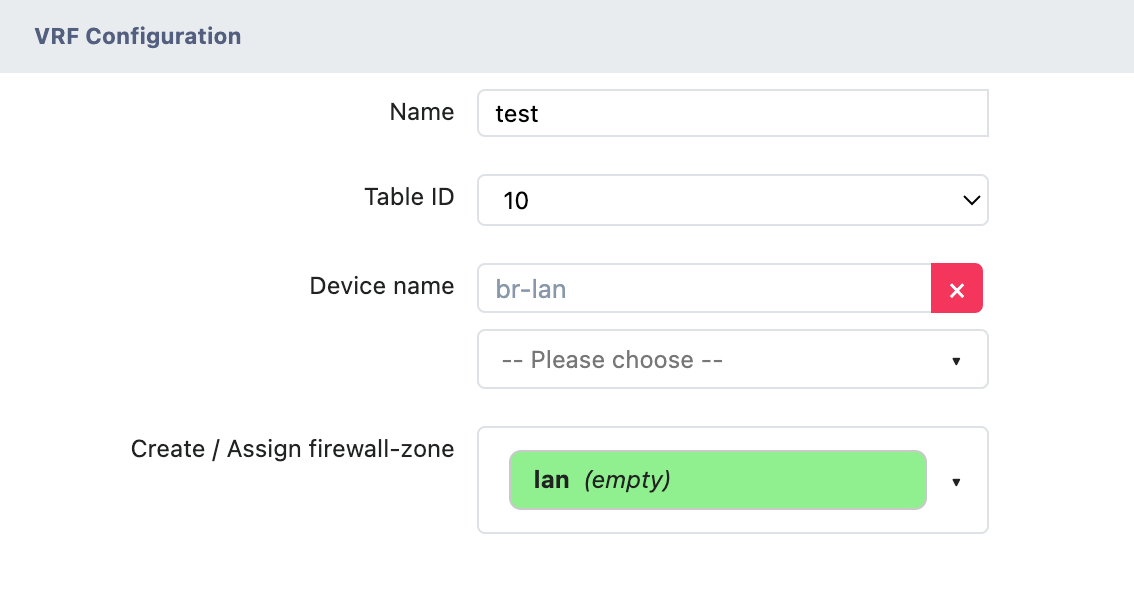
Fill in basic information
- Enter the VRF instance name in the "Name" field
- Select the routing table ID from the "Table ID" drop-down menu
- Select the target interface or bridge in the "Device name" drop-down menu
Configure firewall zone (Optional)
- Select the corresponding firewall zone in the "Create / Assign firewall-zone" dropdown menu
- If a specific area is not required, keep it in the "unspecified" state
VRF Route Addition
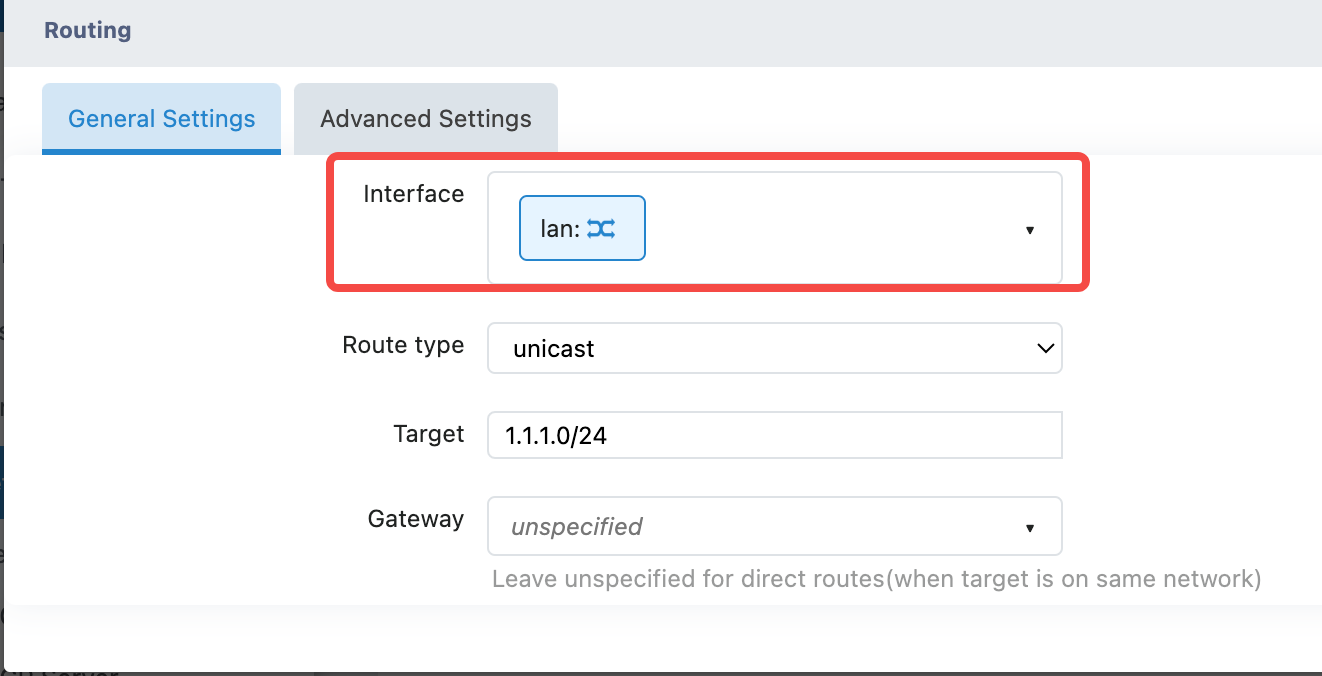
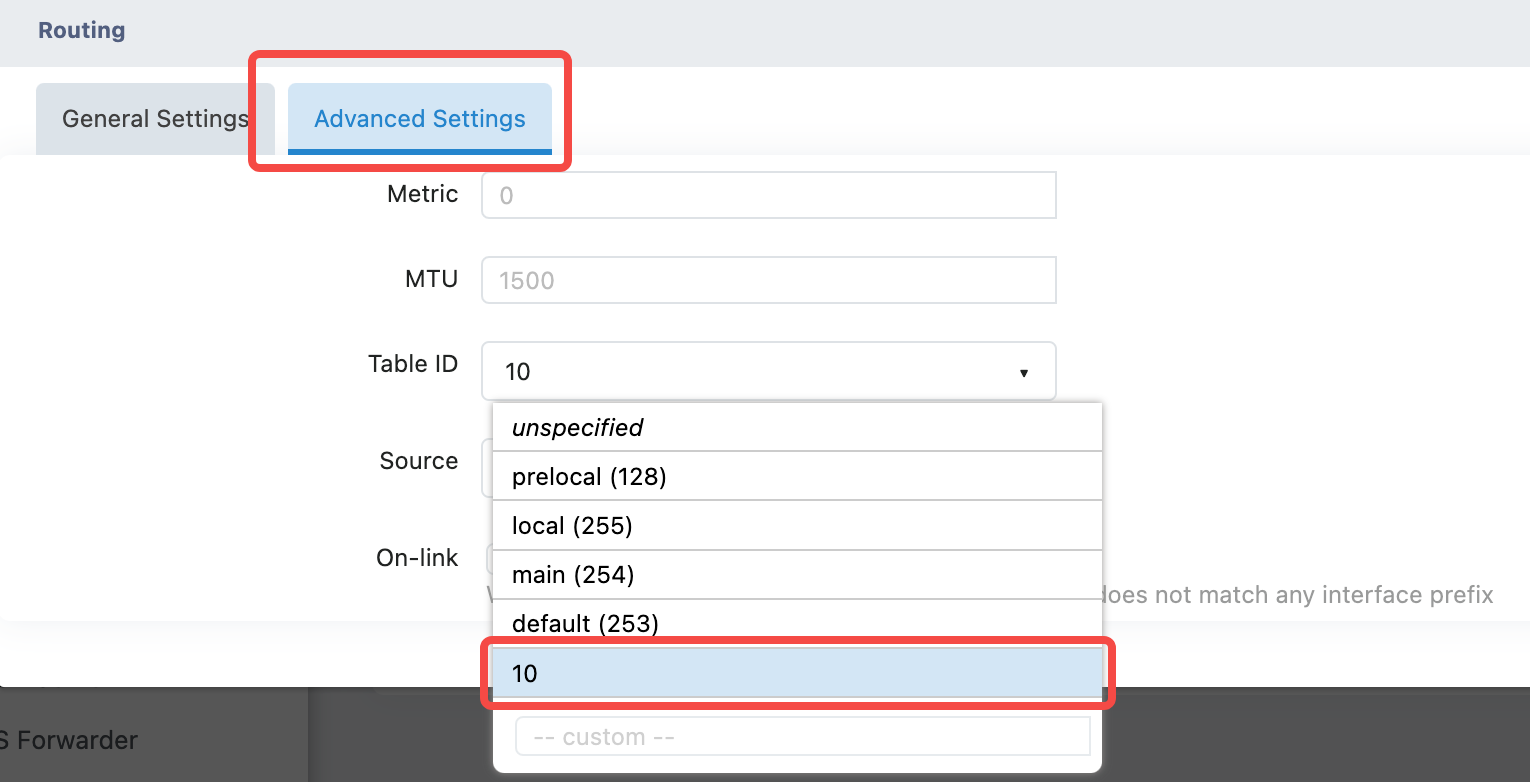
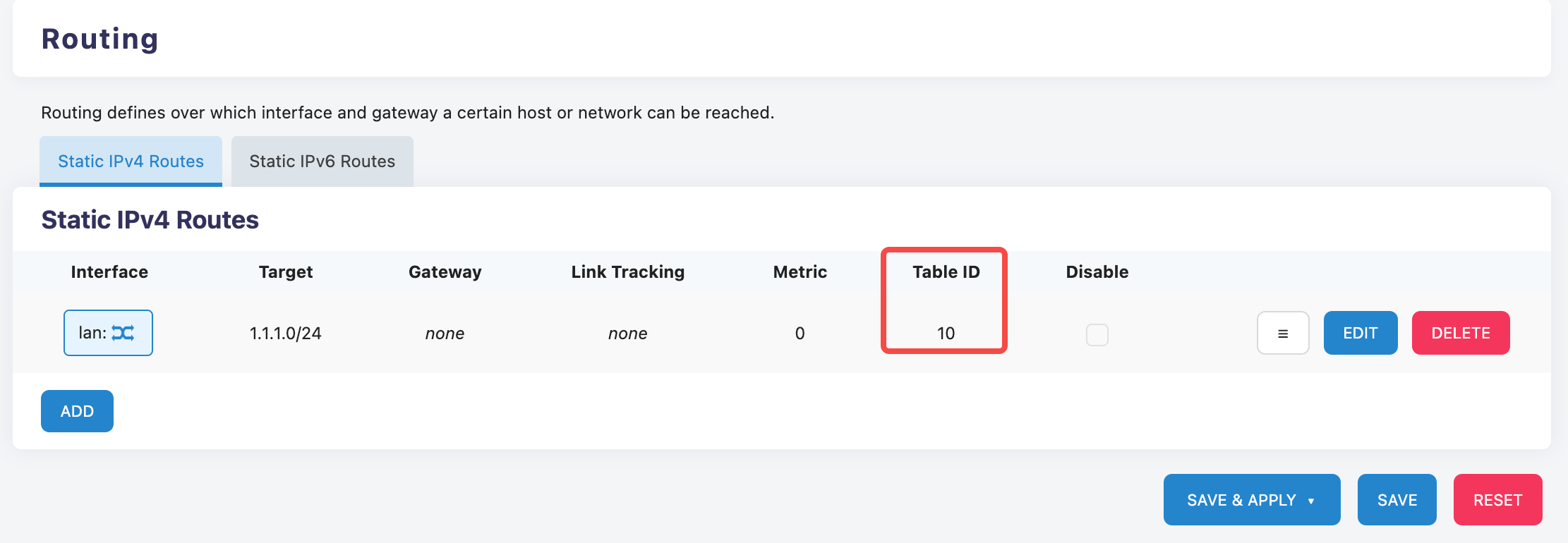
Static Route
On the 'Network>Static Routes' page, when adding a static route, select the VRF interface, and fill in the VRF table ID in the advanced settings to add the VRF route.
Dynamic Routing
On the OSPF configuration page, you can select INSTANCE#2 to 5 to configure the OSPF protocol for VRF. The routing table of each INSTANCE is independent, with INSTANCE#1 being the main routing table.
Routing Table
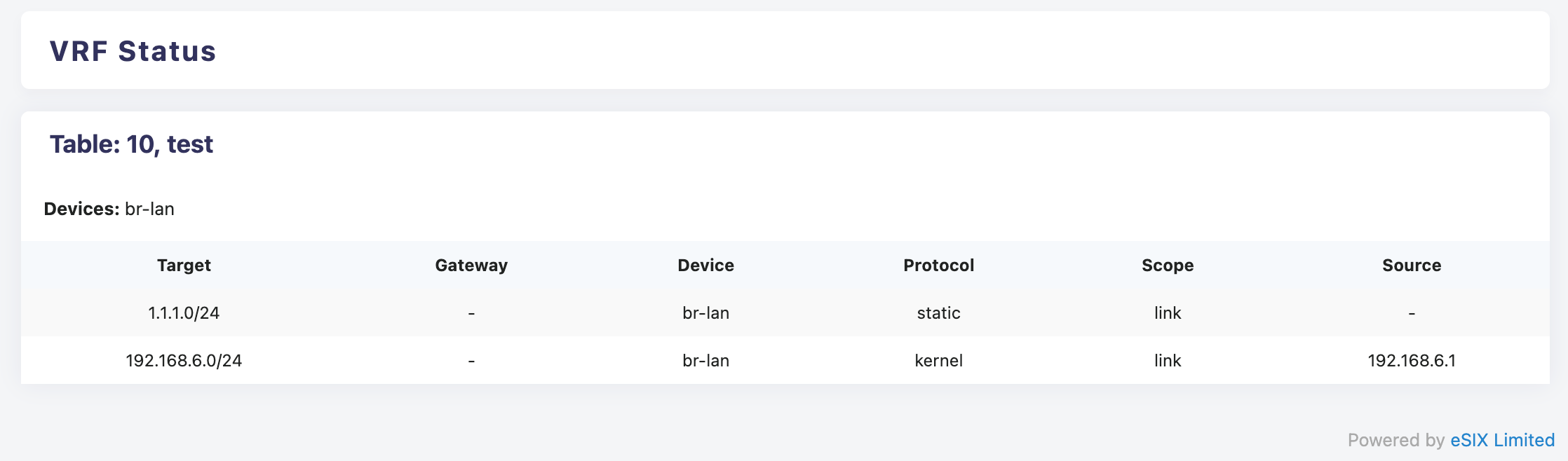
On the 'Status>VRF' page, you can view the VRF routing table
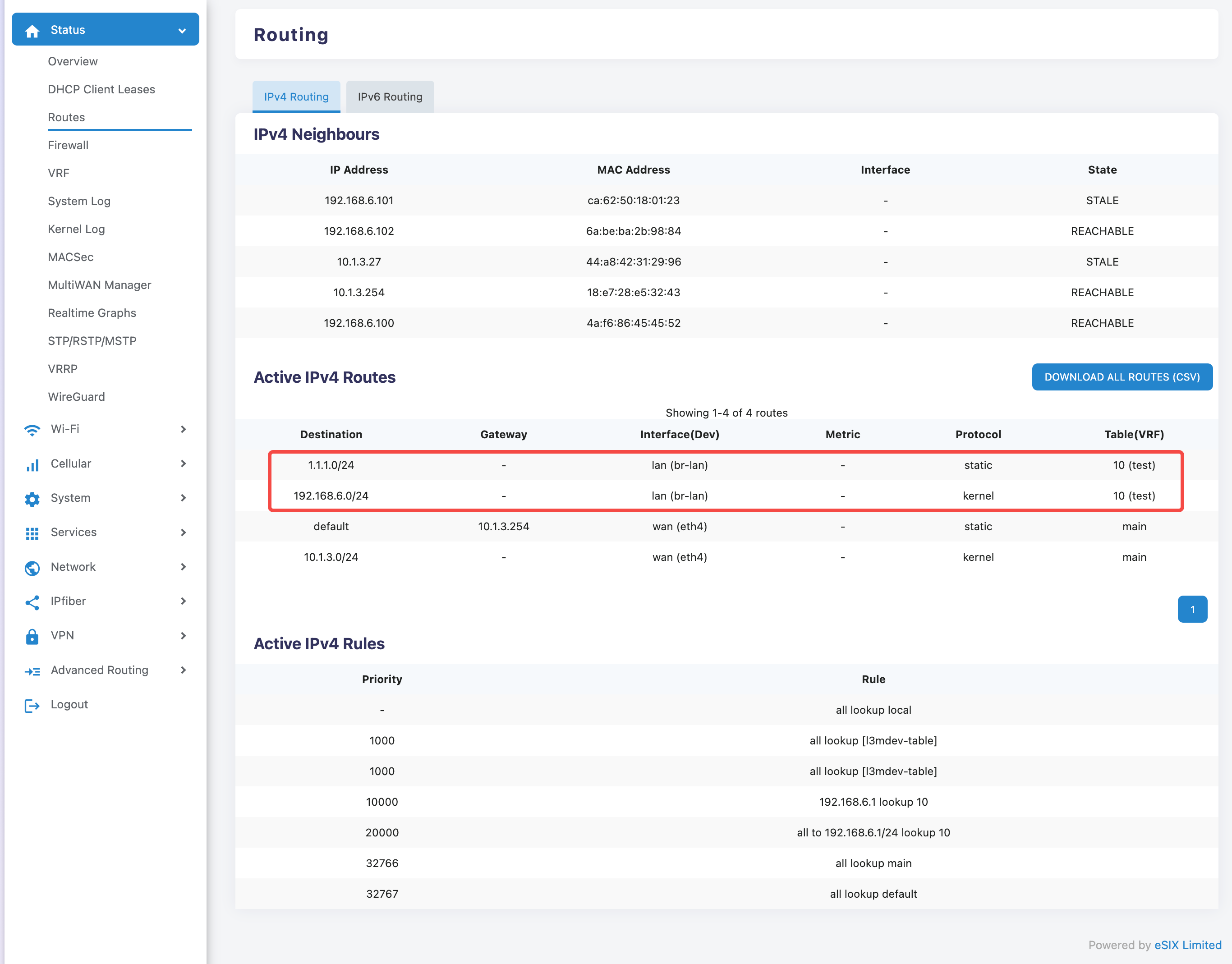
On the 'Status>Routes' page, you can view the routes of VRFs that appear in the total routing table
Precautions
- Route Table ID Uniqueness: Ensure that each VRF instance uses a different Table ID
- Device Compatibility: Confirm that the target device supports VRF functionality
- Firewall Policy: Configure corresponding firewall rules to ensure cyber security
- Configuration Verification: After applying the configuration, it should be verified whether the VRF instance is working properly
Troubleshooting
- If the configuration cannot be saved, check whether all required fields have been filled in correctly
- Confirm that the Table ID does not conflict with existing VRF instances
- Verify whether the selected device is online and supports VRF functionality
By properly configuring VRF, isolation and optimized management of network resources can be effectively achieved.